A septic tank is an underground tank made of concrete, fiberglass, or polymers through which wastewater flows for basic sewage treatment. It holds solid waste while bacteria decompose it. Contact Septic Tank Armadale now!
Septic tanks are custom-sized for each home based on family size and water consumption. An outlet baffle prevents sludge and scum from leaving the tank, and an effluent pipe extends to a drainfield or leach field in the soil.
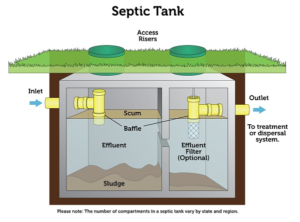
Every time you flush your toilet, shower or use your sinks and washer, wastewater flows through a series of pipes into your septic tank. Your septic tank is a watertight concrete or plastic box that holds your wastewater long enough for solids and liquids to separate. Solid wastes, also known as sludge, sink to the bottom of your septic tank while fats, oils and grease float to the top. Anaerobic bacteria (bacteria that thrive in areas without oxygen) break down the organic matter, resulting in lighter liquids called effluent. The filtered effluent then exits your septic tank through perforated pipes and into your septic system drain field.
Your septic tank has an inlet pipe and an outlet pipe. The inlet pipe transports wastewater from your home, while the outlet pipe transports safer wastewater into your septic system’s drain field. The drain field is a large area of your yard that’s designed to slowly distribute the safe wastewater into the soil.
The liquid that exits your septic tank isn’t fully treated, however. The aeration process breaks down many organic pollutants in your sewage, but some still remain. These chemicals, odors, and heavy metals must be eliminated. Gases generated by bacteria that break down the contaminants are released through a vent in your septic tank roof, usually with a mushroom shape and a charcoal filter to reduce odors.
A septic tank’s sludge and scum layers must be periodically pumped out, usually once every three to five years. A professional septic service company will perform this routine maintenance. If the sludge layer is within six inches of the inlet or the scum layer is more than 12 inches from the outlet, your septic tank needs to be pumped.
Keeping the septic tank in good working condition also requires avoiding flushing items that can cause the septic system to overflow or clog the drain field. Chemical drain openers, bleach and other harsh cleaners should be avoided because they kill the bacteria that keep the septic tank working properly. Garbage disposals should also be used sparingly, since they add to the amount of waste that ends up in your septic tank and drain field.
Installation
The septic tank is a large underground tank where wastewater goes when it leaves your home. It is a treatment system used in areas without centralized sewer systems. Like a miniature treatment facility in your backyard, a septic system is an efficient way to treat household wastewater and separate solid waste from liquid waste.
A septic tank is water-tight and usually made of concrete, fiberglass, or polyethylene. It is buried in the ground and contains a compartment for each drain. Its job is to hold the wastewater long enough to allow solids to settle and float. Solids are then separated from the liquids, which is then pumped into a drain field or leach field of perforated pipes that will slowly filter back into the soil.
In order to determine if your property is suitable for a septic system, a land survey will be conducted by a licensed professional. This will help ensure that the proposed septic tank site is actually within the boundaries of your property, which can avoid expensive legal headaches down the road.
Once the septic tank is installed, it should be covered with a permanent grass cover to prevent surface runoff from polluting the surrounding area. It is also a good idea to keep a map or diagram of the location of your tank, its access ports and check wells, and your drain field to avoid confusion or misplacement over the years. It will also make it easier to locate these components for future septic tank maintenance and repair.
During the installation process, your contractor will need to dig a hole large enough for the septic tank and piping. He will then construct the septic tank with reinforced concrete, or if your property is sandy or gravel, he will construct a fiberglass or plastic tank. The septic tank needs to be buried at least 6 inches below the top of the finished grade to minimize cracking.
It is important to choose a reputable septic system installer for your project. Experienced contractors will have a wealth of knowledge about different types and sizes of tanks and will be able to advise you on the best option for your home or business. They will also be able to pull the necessary permits for your septic system.
Maintenance
When a septic tank is properly maintained, it can last forty years or more without malfunction. On the other hand, improper maintenance can cause wastewater to back up into the home or even into groundwater supplies. This can lead to costly repairs and possible environmental issues.
A septic system has three main components that are essential to its proper function. The first is the tank, which contains bacteria that break down solid waste into sludge and liquid waste for filtration through the absorption field.
Next comes the drain or leach field, which is a series of pipes with holes in them laid in gravel trenches underneath the soil. The water seeps through the gravel and into the soil, where it is absorbed by grass and dirt above. When the septic tank or the drain field fails, the wastewater can flood the house and leak into the ground surface or into toilets and sinks.
The final piece of a septic system is the septic tank inlet pipe and the outlet tee opening, which are connected to the inlet pipe. When the tank is full, the scum layer will rise above the top of the inlet tee and the sludge layer will be within several inches of the bottom of the outlet tee. A septic tank has to be pumped when these levels are too high to prevent the inlet and outlet pipes from becoming clogged.
Homeowners can prevent septic tank problems by keeping the scum and sludge layers as low as possible, scheduling regular pumpings, and using a non-toxic household cleaner or baking soda to clear clogged drains. They should also avoid putting heavy items above the septic tank and drainfield, as excessive weight can shift the soil around the tanks and leach fields and cause them to crack or fail. Finally, it is important to keep records of all septic system work performed. This can help homeowners identify potential problems with their septic systems and make sure the work is completed correctly. Finally, homeowners should be very careful near septic tanks because falling into one can result in death by suffocation or drowning.
Replacement
Your septic tank is an important component of your home sewer system. It stores sewage waste until it can be emptied by a company that offers septic tank pumping. The sewage is then discharged into a drain field, or soil absorption system. From the drain field, wastewater is absorbed into the soil to treat it. Without a functioning septic tank, you could experience sewage backups in your toilets or in groundwater supplies, which are costly and dangerous.
All of the plumbing in your house connects to a sewer line that slopes toward your septic tank. When you flush a toilet, take a shower, wash clothes, or use the dishwasher, wastewater enters the line and flows into your tank. The septic tank is made of concrete or steel and can be built underground or aboveground. It’s often large and rounded, so it doesn’t collect debris on the top that could damage the system.
Inside the septic tank, there are PVC “T”-shaped fittings that extend in and out of the tank. The inlet tee is designed to fit over the scum layer so that hydraulic pressure forces wastewater up and out of the tank. The outlet tee is several inches below the inlet tee to prevent solids from entering your drain field.
Solids can clog the absorption field, reduce its efficiency, and cause it to contaminate groundwater sources. To prevent this, a septic tank may be fitted with an effluent filter, which is placed in the outlet tee of the septic tank to intercept solids before they exit the tank. The filter is relatively inexpensive and far less expensive than replacing the entire drain field.
Your septic tank should be inspected at least once a year to make sure there are no cracks or other structural damage. In addition, the tank must be pumped regularly to ensure that it doesn’t overflow. A septic tank that is overflowing or leaking can pollute your groundwater supply, contaminate soil near the tank, and lead to unpleasant odors in and around the home.
If your septic system is due for replacement, it’s essential to find an experienced contractor who can complete the project quickly and cost-effectively. If you’re considering a septic tank replacement, speak to the installer about financing options. Many companies offer low-interest, long-term loans to help you manage the costs. Additionally, you might be able to qualify for state and local grants or rebates that can offset the initial installation costs.